Key Questions
- How does the American Dream influence mental health?
- What psychological and sociological factors impact an individual's ability to achieve the American Dream?
- How do economic and social pressures shape well-being?
The American Dream & Mental Health
The American Dream can contribute to mental illness due to constant pressures to succeed and live up to societal standards. At the same time, mental health conditions such as depression can hinder people’s ability to pursue the American Dream because symptoms like lack of motivation reduce productivity and goal-directed behavior.
Crossovers
Economic Stressors → Anxiety & Depression
Social Comparison → Lower Self-Esteem (social media boom)
Isolation → Reduced Opportunity
Psychological & Sociological Effects
Psychological Effects: Burnout and identity crisis tied to material success.
Sociological Effects: Inequality, particularly among marginalized groups such as LGBTQ individuals.
Key Statistics
- 63% of people in the LGBTQ community reported feeling down or experiencing depression at least once a week.
Additional U.S. Mental Health Data
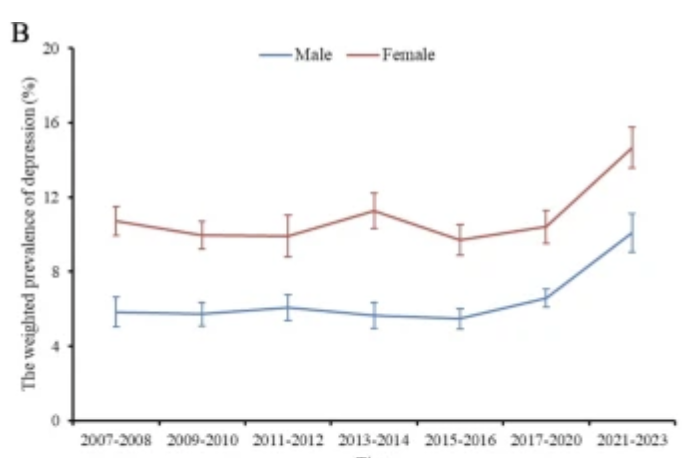
- NHANES 2021–2023: 13.1% of U.S. adolescents and adults reported depression in the past two weeks.
- 87.9% of those with depression reported at least some difficulty with work, home, or social activities.
- 31.2% reported extreme difficulty — directly undermining American Dream milestones like education, opportunity, and upward mobility.
- Income impact:
- Below poverty level: 22.1% depression rate
- At or above 400% of federal poverty level: 7.4% depression rate
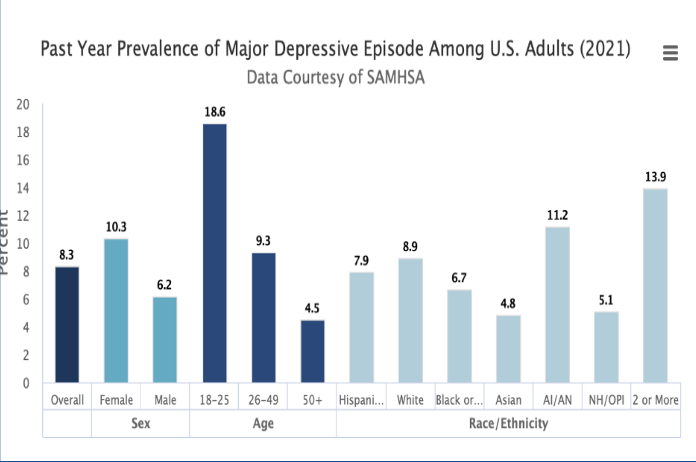
- Gender differences:
- Females: 16.0%
- Males: 10.1%
- Age patterns:
- Adolescents (12–19): 19.2%
- Adults 60+: 8.7%
- Trend: Depression prevalence has increased by 60% over the past decade.
Class Plays & Their Connections
- Fences: Race and socioeconomic status
- Angels in America: Sexuality and societal approval
- Hamilton: Opportunity vs. pressure
- August: Osage County: Family dynamics, happiness, and health
Abbreviations
- NHANES - National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- WHO - World Health Organization
- APA - American Psychological Association
- SAMHSA - Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration